

This type two error results from having a small sample size, or from participants dropping out of the sample. We could avoid this by random sampling and ensuring representativeness of our sample with regards to sample size.Īn inadequate sample size decreases the confidence in our results as we may think there is no significant difference when actually there is.
Non-random selection increases the probability of sampling (selection) bias if the sample does not represent the population we want to study. We can randomly select 3 out of 10 schools as our clustersĪdvantages: Readily doable with most budgets, does not require a sampling frameĭisadvantages: Results may not be reliable nor generalisable
Simple random sampling method example generator#
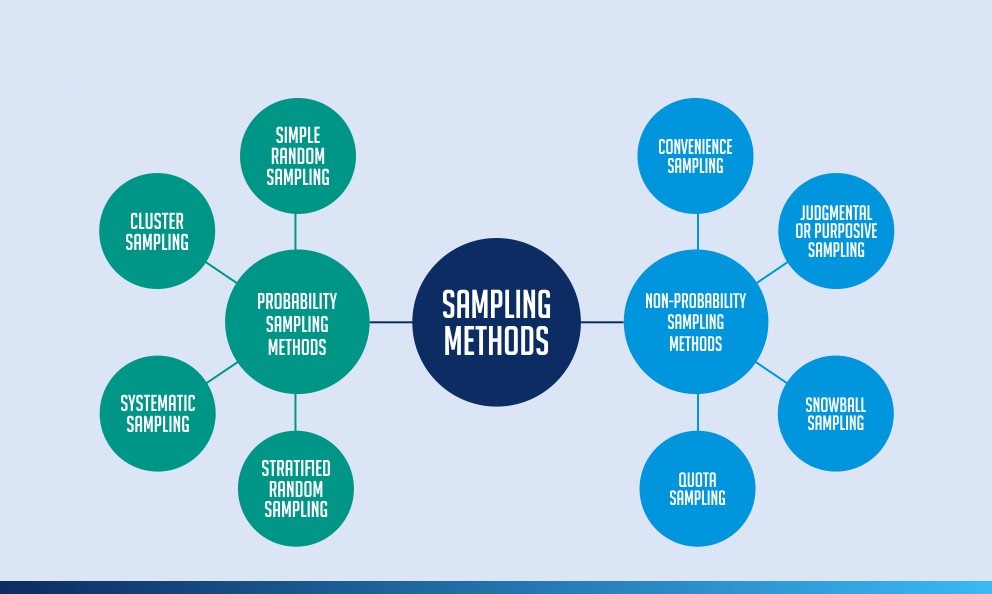
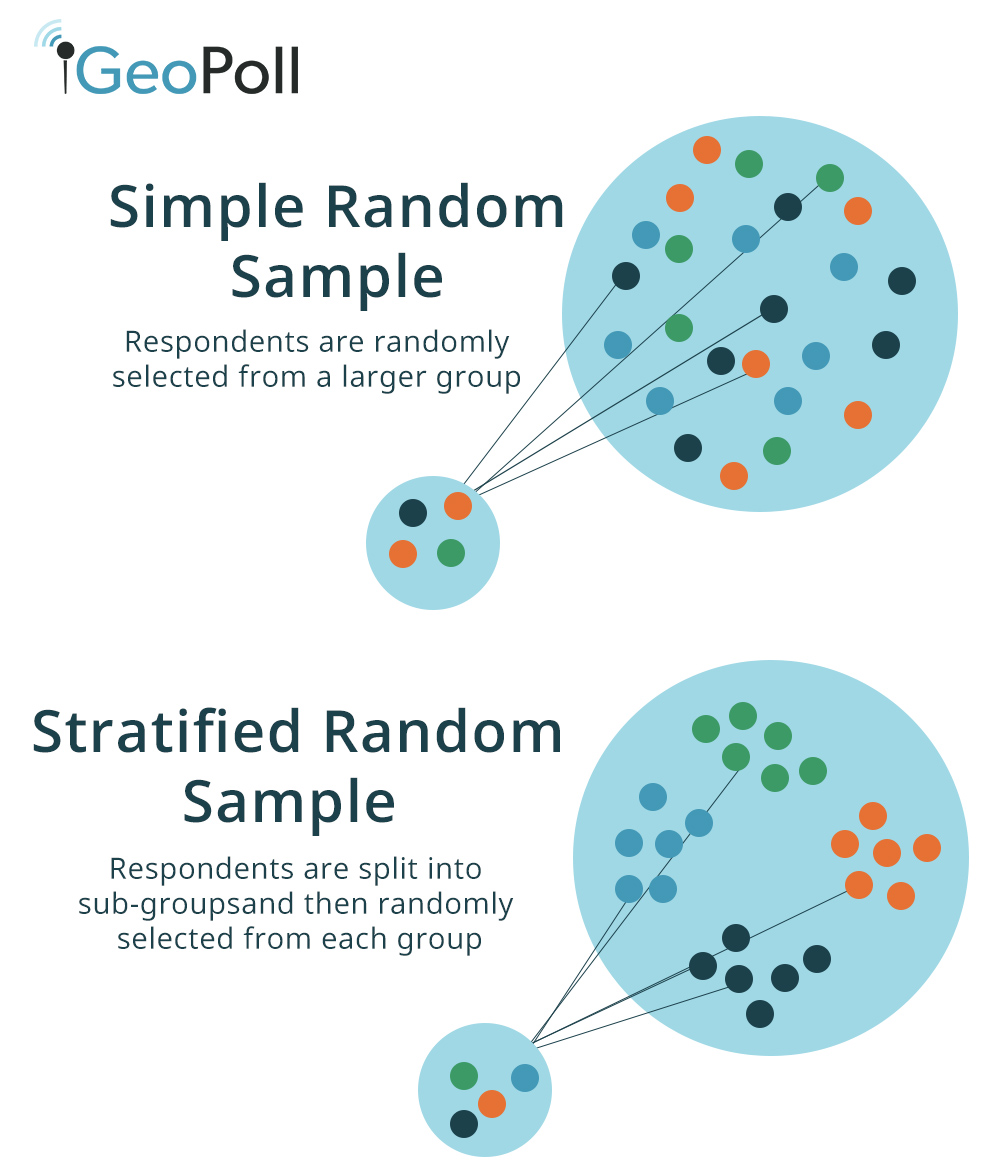
We include everyone in a list and use a random number generator to select the participantsĪdvantages: Generalisable results possible, random sampling, the sampling frame is the whole population, every participant has an equal probability of being selectedĭisadvantages: Less precise than stratified method, less representative than the systematic methodĮxample: Every nth patient entering the out-patient clinic is selected and included in our sampleĪdvantages: More feasible than simple or stratified methods, sampling frame is not always requiredĭisadvantages: Generalisability may decrease if baseline characteristics repeat across every nth participantĮxample: We have a big population (a city) and we want to ensure representativeness of all groups with a pre-determined characteristic such as: age groups, ethnic origin, and genderĪdvantages: Inclusive of strata (subgroups), reliable and generalisable resultsĭisadvantages: Does not work well with multiple variablesĮxample: 10 schools have the same number of students across the county.
Simple random sampling method example trial#
SimpleĮxample: We want to conduct an experimental trial in a small population such as: employees in a company, or students in a college. For the purposes of this blog we will be focusing on random sampling methods. Non-random sampling methods are liable to bias, and common examples include: convenience, purposive, snowballing, and quota sampling. Random sampling examples include: simple, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling. We could choose a sampling method based on whether we want to account for sampling bias a random sampling method is often preferred over a non-random method for this reason. What makes a good sample?Ī good sample should be a representative subset of the population we are interested in studying, therefore, with each participant having equal chance of being randomly selected into the study. In other words, it is a list from which we can extract a sample. What is a sampling frame?Ī sampling frame is a record of the target population containing all participants of interest. However, it would not be feasible to experiment on the whole population, we would need to take a good sample and aim to reduce the risk of having errors by proper sampling technique. In other words, we want to find out if this is a true association, while still aiming for the minimum risk for errors such as: chance, bias or confounding. It is important to understand why we sample the population for example, studies are built to investigate the relationships between risk factors and disease. This tutorial will introduce sampling methods and potential sampling errors to avoid when conducting medical research.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
